Naprapathic Medicine is an advanced healthcare system that integrates Physical (Manual) Medicine, Nutritional Counseling, and Therapeutic Modalities. It specifically targets pain arising from Connective Tissue Disorders, emphasizing a holistic approach to health. Naprapaths are skilled specialists in connective tissue, crucial for supporting and containing all vital structures of the body, including tissues around the spinal column, spinal cord, muscles, organs, and joints. This comprehensive care aims to enhance overall well-being and mobility by addressing the root causes of pain.
Discover Naprapathic Medicine: A Holistic Approach to Pain Relief
The Origins of Naprapathy: A Pioneering Approach to Manual Medicine
Naprapathy, a distinct branch of manual medicine, was founded by Dr. Oakley Smith on November 16th, 1905. This pioneering approach has since evolved to become a key method in treating connective tissue disorders and enhancing overall wellness through specialized techniques.
Dr. Oakley Smith, DN, established the field of Naprapathy on November 16, 1905, a date now officially recognized as National Naprapath Day since 2022. Prior to this designation, the day was affectionately known among Naprapathic Doctors as ‘Ligatite Day,’ celebrating the foundational discoveries in connective tissue manipulation that define Naprapathy.
Naprapathic Doctors: Specialists in Connective Tissue Health
A Naprapath, or Naprapathic Doctor, is a specialist in connective tissue, playing a crucial role in complementary manual medicine. In the 21st century, Naprapaths are celebrated for their holistic, person-oriented approach. They dedicate time to thoroughly explain procedures and conditions to patients, encouraging active participation in adopting healthy lifestyles. This includes proper exercise, correct posture, sound body mechanics, and optimal nutrition, all essential for maintaining connective tissue health.
“A Connective Tissue Specialist expertly identifies, evaluates, and treats Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs), focusing on enhancing tissue health and function.
Understanding Connective Tissue: The Structural Framework of the Body
Connective tissue is a fundamental type of biological tissue that plays a crucial role in linking and supporting the structures of the body. This includes connecting bones to each other or supporting tissues. Key types of connective tissue include cartilage, bone, adipose (fat), and blood, each serving unique functions.
Connective tissues are essential for providing support and structure to other tissues and organs. They are involved in storing fat, transporting nutrients and other substances between tissues and organs, and aiding in the repair of damaged tissues. Structurally, connective tissue is characterized by relatively few cells embedded in an amorphous matrix, often reinforced with collagen or other fibers. This group encompasses a variety of tissues, including cartilaginous, fatty, and elastic types.
Connective Tissue Disorders are characterized by abnormally rigid or contracted ligaments, tendons, and muscles, which can significantly interfere with nerve conduction and the circulation of blood and lymph. These disruptions often result in pain and inflammation in the affected areas of the body.
Naprapathic Medicine offers successful treatment for a variety of musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders, including:
These conditions are effectively managed through Naprapathic techniques that focus on alleviating pain and restoring normal function, providing patients with relief and improved quality of life.
Understanding Connective Tissue Disorders and Naprapathic Treatment Options
Common Causes of Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs)
Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs) can arise from a variety of causes, including but not limited to:
Understanding these causes can help in the prevention and management of CTDs, providing a foundation for healthier living and workplace practices.
Naprapathic Medicine: A Comprehensive Approach to Tissue Health
Naprapathic Medicine employs a holistic approach to health, focusing on the correction and restoration of tissue health through both manual medicine and nutritional counseling. This dual approach significantly enhances treatment outcomes for Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs).
Key Approaches in Naprapathic Medicine:
Physical Medicine:
Manual Modalities:
Advanced Therapeutic Modalities:
Comprehensive Nutritional Counseling:
The integration of manual techniques with nutritional strategies not only improves the management of CTDs but also contributes to a growing demand for qualified, licensed Naprapaths. Individuals interested in a career that combines expertise in manual medicine with nutritional counseling will find Naprapathic Medicine a dynamic and fulfilling field.
Starting annual salaries for Naprapathic Doctors can reach up to $75,992, equivalent to $36.50 per hour, with potential earnings ranging up to $106,614 annually, or $51.25 per hour. This competitive compensation reflects the growing demand for qualified, licensed Naprapaths. Individuals interested in a career specializing in manual medicine and nutritional counseling will discover that Naprapathic Medicine offers a dynamic and rewarding professional opportunity.
Career Opportunities and Salaries in Naprapathic Medicine
NCNM University’s Health Clinics and hospitals are set to enhance their healthcare offerings by employing licensed Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) with starting annual salaries of $80,000. This competitive starting salary reflects the growing demand and value of qualified Naprapaths in the healthcare industry.
The Doctor of Naprapathy (DN) Program offers a comprehensive 4-year curriculum, with an accelerated 3-year option available. Additionally, candidates with advanced degrees may have the opportunity to complete the DN program in as little as 2.5 years. Prospective students are encouraged to contact universities directly to obtain specific details regarding the duration of the Doctor of Naprapathy (DN) Program. Completion times can vary based on individual circumstances and academic background.
While the majority of Naprapathic Doctors operate in private practices, an increasing number of Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) are expanding their reach into hospitals, urgent care centers, and medical group settings.
NCNM University and NCNMU Health are leading the charge in creating more strategic relationships with hospitals and other universities to expand career opportunities for its graduates. This initiative ensures that the opportunities available extend beyond just NCNMU and NCNMU Health, broadening the potential for DNs to impact patient health in diverse medical environments.
This shift is indicative of the growing recognition of Naprapathic Medicine within the broader medical community and its effectiveness in treating a wide range of conditions. As Naprapathic Medicine continues to integrate with mainstream healthcare, DNs enjoy a broader scope of practice and the ability to impact patient health in diverse medical environments.
Naprapathic Medicine, a globally recognized health practice, ranks as the second largest form of medicine in Scandinavia. It is widely practiced in Sweden, Finland, and Norway, with established educational institutions in both Sweden and Finland. Additionally, Naprapathy has expanded its reach to Spain, where another school exists, and continues to grow in popularity in countries like Canada, China, and India.
US Licensing for Naprapathy
Naprapathy is a licensed profession in several states, reflecting its growing acceptance and recognition in the healthcare field. Currently, practitioners can obtain licenses in:
This licensure allows Naprapaths to practice and contribute significantly to health and wellness in these regions.
Professional Licensing and Regulatory Framework for Naprapathy in the United States
Naprapathy, recognized as a licensed healthcare profession, is regulated through specific state legislations and practice acts. Currently, Illinois, New Mexico, Nevada, and Ohio have established Naprapathic Practice Acts (NPA), which govern the practice of Naprapathy. Notably, Ohio also incorporates a grandfathered license system, reflecting its unique regulatory approach.
In addition to state-specific NPAs, the Federal Safe Harbor Laws are enacted in several states to protect practitioners of alternative and complementary medicine. These laws are currently in place in:
It is crucial to understand that in states with Naprapathic Practice Acts, such as Illinois, New Mexico, Nevada, and Ohio, these acts supersede the Federal Safe Harbor Laws. This means that licensed Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) from states like Illinois seeking to practice in another state with an NPA must undergo a license reciprocation process, unlike in Safe Harbor states where their existing licenses may be recognized with full rights and privileges.
Furthermore, there is pending legislation for Safe Harbor Laws in numerous states, including:
This pending legislation could significantly expand the legal recognition and practice rights for Naprapaths across the nation.
The evolving legal landscape offers a dynamic and promising future for the growth and professional recognition of Naprapathy as a critical component of healthcare in the United States.
State Licensing for Naprapathy
Naprapathy is a licensed profession in several states, reflecting its growing acceptance and recognition in the healthcare field. Currently, practitioners can obtain licenses in:
This licensure allows Naprapaths to practice and contribute significantly to health and wellness in these regions.
Professional Licensing and Regulatory Framework for Naprapathy in the United States
Naprapathy, recognized as a licensed healthcare profession, is regulated through specific state legislations and practice acts. Currently, Illinois, New Mexico, Nevada, and Ohio have established Naprapathic Practice Acts (NPA), which govern the practice of Naprapathy. Notably, Ohio also incorporates a grandfathered license system, reflecting its unique regulatory approach.
In addition to state-specific NPAs, the Federal Safe Harbor Laws are enacted in several states to protect practitioners of alternative and complementary medicine. These laws are currently in place in:
It is crucial to understand that in states with Naprapathic Practice Acts, such as Illinois, New Mexico, Nevada, and Ohio, these acts supersede the Federal Safe Harbor Laws. This means that licensed Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) from states like Illinois seeking to practice in another state with an NPA must undergo a license reciprocation process, unlike in Safe Harbor states where their existing licenses may be recognized with full rights and privileges.
Furthermore, there is pending legislation for Safe Harbor Laws in numerous states, including:
This pending legislation could significantly expand the legal recognition and practice rights for Naprapaths across the nation.
The evolving legal landscape offers a dynamic and promising future for the growth and professional recognition of Naprapathy as a critical component of healthcare in the United States.
Click here to see list of States and contacts.
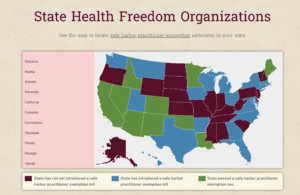
Practicing Naprapathy Across the U.S. Under the Health Care Freedom Act
Licensed Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) have the opportunity to practice across various states under the Health Care Freedom Act of 2017, also known as the Federal Safe Harbor Law. This act currently includes states such as:
Additionally, there are 16 other states with pending legislation aiming to join the Health Care Freedom Act, further expanding the practice landscape for Naprapathy. These states are (Washington, Montana, Utah, Texas, Arkansas, Iowa, Wisconsin, Michigan, New York, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Hawaii, and Ohio).
To practice under this act, Naprapathic Doctors must ensure compliance with two key requirements:
Active DN License: It is essential to hold a current and active DN license, which is currently available only in Illinois and New Mexico. Obtaining this license requires passing specific examinations.
State-specific Reciprocity: Practitioners must contact the relevant state authorities to understand the process for reciprocating their license to practice under the Health Care Freedom Act in the state of interest.
These provisions facilitate the expansion of Naprapathy, allowing practitioners to offer their specialized services across a broader geographic area.
Click here to see list of States and contacts.

State Organizations – National Health Freedom Action
State Licensing for Naprapathy
Naprapathy is a licensed profession in several states, reflecting its growing acceptance and recognition in the healthcare field. Currently, practitioners can obtain licenses in:
This licensure allows Naprapaths to practice and contribute significantly to health and wellness in these regions.
Professional Licensing and Regulatory Framework for Naprapathy in the United States
Naprapathy, recognized as a licensed healthcare profession, is regulated through specific state legislations and practice acts. Currently, Illinois, New Mexico, Nevada, and Ohio have established Naprapathic Practice Acts (NPA), which govern the practice of Naprapathy. Notably, Ohio also incorporates a grandfathered license system, reflecting its unique regulatory approach.
In addition to state-specific NPAs, the Federal Safe Harbor Laws are enacted in several states to protect practitioners of alternative and complementary medicine. These laws are currently in place in:
It is crucial to understand that in states with Naprapathic Practice Acts, such as Illinois, New Mexico, Nevada, and Ohio, these acts supersede the Federal Safe Harbor Laws. This means that licensed Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) from states like Illinois seeking to practice in another state with an NPA must undergo a license reciprocation process, unlike in Safe Harbor states where their existing licenses may be recognized with full rights and privileges.
Furthermore, there is pending legislation for Safe Harbor Laws in numerous states, including:
This pending legislation could significantly expand the legal recognition and practice rights for Naprapaths across the nation.
The evolving legal landscape offers a dynamic and promising future for the growth and professional recognition of Naprapathy as a critical component of healthcare in the United States.
Practicing Naprapathy Across the U.S. Under the Health Care Freedom Act
Licensed Doctors of Naprapathy (DNs) have the opportunity to practice across various states under the Health Care Freedom Act of 2017, also known as the Federal Safe Harbor Law. This act currently includes states such as:
Additionally, there are 16 other states with pending legislation aiming to join the Health Care Freedom Act, further expanding the practice landscape for Naprapathy. These states are (Washington, Montana, Utah, Texas, Arkansas, Iowa, Wisconsin, Michigan, New York, Massachusetts, Connecticut, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Hawaii, and Ohio).
To practice under this act, Naprapathic Doctors must ensure compliance with two key requirements:
Active DN License: It is essential to hold a current and active DN license, which is currently available only in Illinois and New Mexico. Obtaining this license requires passing specific examinations.
State-specific Reciprocity: Practitioners must contact the relevant state authorities to understand the process for reciprocating their license to practice under the Health Care Freedom Act in the state of interest.
These provisions facilitate the expansion of Naprapathy, allowing practitioners to offer their specialized services across a broader geographic area.
Click here to see list of States and contacts.

Requirements for Obtaining a DN License in Naprapathy
To become a licensed Doctor of Naprapathy (DN), candidates must undergo a rigorous testing process. Here are the essential steps to obtaining a DN license:
Contact a Licensing State: Candidates should reach out to a state where DN licenses are issued. Currently, DN licenses are available in Illinois (IL), New Mexico (NM), and Nevada (NV).
Licensing Examination: Aspiring Naprapaths must register for and pass the state-specific licensing examination. It is advisable to contact state-approved schools or institutions for guidance and preparation assistance.
Licensing Assistance with NCNM University: Enroll in NCNMU’s DN Bridge program, a crucial first step for securing a DN license in states like Illinois. This program is tailored for candidates with DN degrees or equivalent qualifications from recognized institutions. Completing the DN Bridge program at NCNMU awards you a DN degree and provides the necessary transcript for the Illinois DN licensing exam, aligning with the requirements faced by our regular DN candidates. This streamlined process is designed to efficiently prepare DN Bridge program candidates for the DN licensing exam, ensuring eligibility under safe harbor laws (if the candidate chooses to practice in those select states with safe harbor practitioner exemptions). For comprehensive guidance and to verify if your institution is recognized, click here for NCNMU’s Policy on licensing assistance. If your school is not listed in NCNMU’s Policy, it indicates that we do not recognize the institution, and you will need to follow the traditional path to obtain your DN degree through our university, adhering to current admission standards.
By following these steps, candidates can navigate the requirements and successfully obtain a DN license, paving the way for a professional career in Naprapathy.
Yes.
Most major private health insurance providers offer coverage for Naprapathic Services. If Naprapathic Services are not included, patients will need to contact their insurance companies to request coverage for related physical medicine services, such as physical therapy and rehabilitation (as Naprapathic treatment incorporates such), ensuring access to essential Naprapathic care.
Naprapathic Doctors provide direct access care, and most health insurance plans cover Naprapathic Services without the need for a referral. No physician referral is required to receive Naprapathic care; however, it is common to obtain referrals through professional courtesy, collaborative healthcare practices, or at the patient’s request. In cases of personal injury, collaboration or a referral from a physician may be necessary.
Common diagnostic exams covered by most health insurance plans include, but are not limited to,
Explore our ‘Find A Naprapath’ section to discover Naprapathic Doctors categorized by their credentials. Our listings include :
An ANA Certified Licensed Naprapathic Doctor holds a valid license, including those with limited scope, issued through the American Naprapathic Association. These practitioners maintain active, good-standing memberships with the ANA, fulfill state-specific continuing education requirements, and adhere to all regulatory compliance standards to ensure both patient and practitioner safety, as endorsed by the American Naprapathic Association.
The distinction between an ANA Certified Licensed Naprapathic Doctor and a Licensed Naprapathic Doctor lies in the certification process. While both hold licensure, only ANA Certified Licensed Naprapathic Doctors have their compliance with statutes and policies verified by the American Naprapathic Association, ensuring adherence to established professional standards.
A Naprapath, or Naprapathic Doctor (also described as Doctor of Naprapathy-DN), specializes as a Connective Tissue Specialist, distinguishing them from Naturopaths (ND). They focus on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs). Connective tissue, which includes structures like ligaments that connect bones to each other, is found throughout the entire body. Naprapaths are skilled in correcting and restoring the health of various tissues, including connective, nerve, muscle, and bone tissues. Their treatment methods encompass both manual techniques and internal approaches through nutrition to enhance tissue health.
Key Approaches in Naprapathic Medicine:
Physical Medicine:
Manual Modalities:
Advanced Therapeutic Modalities:
Comprehensive Nutritional Counseling:
The integration of manual techniques with nutritional strategies not only improves the management of CTDs but also contributes to a growing demand for qualified, licensed Naprapaths. Individuals interested in a career that combines expertise in manual medicine with nutritional counseling will find Naprapathic Medicine a dynamic and fulfilling field.
A Naprapath, or Naprapathic Doctor, specializes as a Connective Tissue Specialist, distinctly different from Chiropractors (DC). They focus on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs). Connective tissue, which includes structures like ligaments that connect bones to each other, is integral to the entire body. Naprapaths excel in correcting and restoring the health of various tissues, including connective, nerve, muscle, and bone tissues, through manual techniques and nutritional approaches to improve overall tissue health. A distinctive aspect of Naprapathic care is the use of gentle, low-velocity manipulation and correction techniques, combined with a comprehensive nutritional scope. This holistic approach, which includes both naprapathic treatment and connective tissue manipulation, is separate yet complementary, setting Naprapathic care apart from the often more forceful adjustments and narrower focus associated with chiropractic treatments.
Key Approaches in Naprapathic Medicine:
Physical Medicine:
Manual Modalities:
Advanced Therapeutic Modalities:
Comprehensive Nutritional Counseling:
The integration of manual techniques with nutritional strategies not only improves the management of CTDs but also contributes to a growing demand for qualified, licensed Naprapaths. Individuals interested in a career that combines expertise in manual medicine with nutritional counseling will find Naprapathic Medicine a dynamic and fulfilling field.
The historical roots of Naprapathy trace back to Dr. Oakley Smith, a former chiropractor who studied under the founder of chiropractic, D.D. Palmer. Smith’s extensive anatomical studies led him to discover the significant role of connective tissue in pain disorders, a discovery that marked the birth of Naprapathy on November 16, 1905.
“Oakley Smith’s journey and departure from chiropractic medicine are vividly detailed in “The Chiropractor’s Protégé: The Untold Story of Oakley G. Smith’s Journey with D.D. Palmer in Chiropractic’s Founding Years” by Dr. Timothy J. Faulkner. Based on Smith’s journals, letters, advertisements, and other rare documents, Faulkner provides a new glimpse into the earliest moments of chiropractic’s formation. This book, enriched with rare photographs and first-hand accounts, many previously unpublished, offers a unique contribution to the history of chiropractic.”
“O.G. Smith spent more time with D.D. Palmer than any other student besides B.J. Palmer. Over the course of nearly four years, Smith played an important role in the birth of chiropractic as a science. Based on Smith’s journals, letters, advertisements, and other rare documents, Timothy J. Faulkner provides a new glimpse into the earliest moments of chiropractic’s formation. Through rare photographs and first-hand accounts, many of which have never been published before Faulkner shares Oakley G. Smith with the reader. The book is a treasure and includes photos of D.D. Palmer that were found along with Smith’s journal as well as stories and anecdotes about the founder of chiropractic that are refreshing and fascinating. This book is a unique contribution to the history of chiropractic. The Chiropractor’s Protégé: The Untold Story of Oakley G. Smith’s Journey with D.D. Palmer in Chiropractic’s Founding Years by Dr. Timothy J. Faulkner, is a must have for anyone interested in the earliest days of chiropractic. Faulkner’s research and the discovery of the OG Smith papers rewrites the founding days of chiropractic and offers new insights into D.D. Palmer and his first students. O.G. smith was probably his 10th student as well as the chiropractor’s protégé.”
Dr. Oakley Smith credits what he learned from Bohemians in Iowa as he developed a charting system for Naprapathic evaluation, technique, and treatment. Smith still hopeful, authored “Modernized Chiropractic,” which laid the groundwork for Naprapathy. Despite his hopes for acceptance within the chiropractic community, his findings were rejected, leading to the end of his professional relationship with D.D. Palmer. Smith developed the word “Naprapathy”, derived from the word “Napravit,” which means to correct suffering. This finding was Smith’s official departure from chiropractic medicine. He left Iowa and established roots in Chicago, IL, beginning the Oakley Smith College of Naprapathy on North Marshfield Ave. The first school, chartered in 1908 in Chicago, Illinois, was named the Oakley Smith School of Naprapathy, evolving into the Chicago College of Naprapathy in 1912. Another significant institution, the National College of Naprapathy, was founded in Chicago in 1949. The two schools merged in 1971 to form the Chicago National College of Naprapathy, later evolving into the National College of Naprapathic Medicine, and exist today as NCNM University. This rich history further solidifies the unique path of Naprapathic medicine separate from its chiropractic and osteopathic contemporaries.
A Naprapath, or Naprapathic Doctor, specializes as a Connective Tissue Specialist, offering a highly effective, non-invasive alternative to traditional medical treatments. Unlike Osteopathic Physicians (DOs) whose training in the United States mirrors that of Medical Doctors (MDs) with a heavy emphasis on pharmacology and surgery, Naprapaths focus exclusively on manual manipulation and nutritional guidance. This approach is particularly relevant today as it aligns with the growing patient demand for natural, drug-free pain management solutions amidst the opioid crisis.
Naprapaths are experts in the identification, evaluation, and treatment of Connective Tissue Disorders (CTDs) through gentle, low-velocity manipulation and correction techniques. These methods, combined with a comprehensive nutritional scope, not only address the symptoms of pain but also aim to restore overall tissue health without the risks associated with invasive procedures and pharmaceutical interventions. This holistic approach ensures that patients receive care that is both effective and aligned with their preferences for less aggressive treatment options.
In an era where many patients are seeking alternatives to traditional medical interventions, Naprapathy offers a promising solution by focusing on natural healing processes and personalized care, setting it apart as a preferred choice for those looking to manage pain and improve their health without resorting to medications or surgery.
While Naprapathy offers a distinct, non-invasive approach to healthcare, it also complements the broader medical expertise of Osteopathic Physicians (DOs). Together, Naprapaths and DOs can form a synergistic partnership, combining the strengths of manual manipulation and holistic nutrition with the comprehensive medical knowledge of osteopathy. This collaboration enhances patient care by providing a multifaceted approach that addresses both specific tissue disorders and overall health, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and personalized treatment possible. In this way, Naprapathy not only stands as a valuable healthcare practice on its own but also as a vital component of integrated medical care.
Key Approaches in Naprapathic Medicine:
Physical Medicine:
Manual Modalities:
Advanced Therapeutic Modalities:
Comprehensive Nutritional Counseling:
The integration of manual techniques with nutritional strategies not only improves the management of CTDs but also contributes to a growing demand for qualified, licensed Naprapaths. Individuals interested in a career that combines expertise in manual medicine with nutritional counseling will find Naprapathic Medicine a dynamic and fulfilling field.
Enroll in a school that offers the Doctor of Naprapathy program.
